| 1. | The characteristics of life
|
_______________ Nutrition【營養】
|
|
_______________ Respiration【呼吸】
|
|
_______________ Reproduction【繁殖】
|
Organisms【生物】
|
_______________ Excretion【排泄】
|
|
_______________ Growth
|
_______________ Movement【移動 】
|
_______________ Sensitivity【靈敏度】
|
Organisms
- _______________ Nutrition【營養】
- _______________ Reproduction【繁殖】
- _______________ Growth
- _______________ Movement【移動 】
- _______________ Sensitivity【靈敏度】
- _______________ Excretion【排泄】
- _______________ Respiration【呼吸】
|
| 2. | Food requirements of humans
Why do we need food? Food provides us with :
- _______________ energy to keep our body warm and support daily activities【支持日常活動】;
- _______________ raw materials for growth and repair【修復】 of body tissues【身體組織】;
- _______________ substances that keep us healthy.
The seven major food substances are:
Primary food substances【基本食物物質】 that are essential【必需】 to life
- _______________ carbohydrates【碳水化合物】
- _______________ lipids【血脂】
- _______________ proteins【蛋白質】
- _______________ water
Protective food substances【保護性食物物質】 that keep us healthy and help prevent diseases.
- _______________ vitamins【維他命 】
- _______________ minerals【礦物質】
- _______________ dietary fibre【膳食纖維】
|
| 3. | Carbohydrates【碳水化合物】
Carbohydrates are organic substances【有機物質】 which are made of _______________ carbon, _______________ hydrogen and _______________ oxygen.
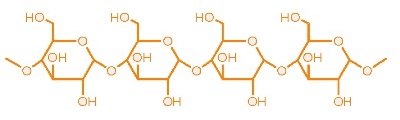
There are three major types of carbohydrates – _______________ monosaccharides, _______________ disaccharides and _______________ polysaccharides, which differ in their molecular complexity【分子復雜性】.
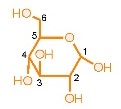
Monosaccharides
e.g. glucose【葡萄糖】 and fructose【果糖】 in fruits, galactose【半乳糖】
- _______________ small molecules【小分子】 -> properties【特質】
- _______________ soluble【溶於】 in water -> properties
- readily absorbed【吸收】 in the _______________ intestines【腸】
- transported【輸送 】 in the _______________ blood to every part of the body
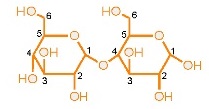
Disaccharides
e.g. sucrose【蔗糖】 in table sugar, lactose【乳糖】 in milk, maltose【麥芽糖】
- _______________ too large to be absorbed directly【直接地】 in the intestines
Polysaccharides
e.g. _______________ starch【澱粉】 in cereals, taros, maize and potatoes
- made up of _______________ long chains【長鏈】 of _______________ glucose unit【葡萄糖單位】
- size is _______________ too large for absorption【吸收】
- broken down into【分解成】 monosaccharides by _______________ hydrolysis【水解】
|
| 4. | Metabolism【代謝】 Of Carbohydrates【碳水化合物】 In The Human Body
Monosaccharides
e.g. glucose
- is broken down during _______________ respiration to release【釋放】 energy.
- provides immediate【即時】 _______________ energy source【能量源】 for body activities.
|
glucose【葡萄糖】
|
+ |
oxygen
|
Respiration【呼吸】
————-> |
_______________ energy
|
+ |
_______________ carbon dioxide
|
+ |
_______________ water
|
glucose【葡萄糖】 + oxygen –> (Respiration【呼吸】) –> _______________ energy + _______________ carbon dioxide + _______________ water
Disaccharides
- broken down into【分解成】 _______________ monosaccharides before absorption【吸收】 by hydrolysis【水解】.
- for hydrolysis to happen, _______________ suitable enzyme is required.
|
maltose【麥芽糖】
|
+ |
water
|
maltase【麥芽糖酶】
————-> |
_______________ glucose【葡萄糖】
|
+ |
_______________ glucose【葡萄糖】
|
|
sucrose【蔗糖】
|
+ |
water
|
sucrase【蔗糖酶】
————-> |
_______________ glucose【葡萄糖】
|
+ |
_______________ fructose【果糖】
|
|
lactose【乳糖】
|
+ |
water
|
lactase【乳糖酶】
————-> |
_______________ glucose【葡萄糖】
|
+ |
_______________ galactose【半乳糖】
|
maltose【麥芽糖】 + water –> (maltase【麥芽糖酶】) –> _______________ glucose【葡萄糖】 + _______________ glucose【葡萄糖】
sucrose【蔗糖】 + water –> (sucrase【蔗糖酶】) –> _______________ glucose【葡萄糖】 + _______________ fructose【果糖】
lactose【乳糖】 + water –> (lactase【乳糖酶】) –> _______________ glucose【葡萄糖】 + _______________ galactose【半乳糖】
Polysaccharides
- different types of enzymes are required to break down a _______________ starch molecule【澱粉分子】 to form glucose.
Part of a starch molecule
_______________ amylase catalyses【催化】 the breakdown of starch to maltose
maltose molecules
_______________ maltase【麥芽糖酶】 catalyses【催化】 the breakdown of maltose to glucose
glucose molecules
|
| 5. | Functions Of Carbohydrates In The Human Body
- as main source of _______________ energy (especially glucose) for metabolism【代謝】 in the body
- 1g of carbohydrates -> 17.1kj of energy
- as energy storage
- excess【過多的】 carbohydrates are converted【轉化為】 to _______________ glycogen【糖原】 or _______________ lipids【血脂】
- glycogen: stored in _______________ liver【肝】 and _______________ skeletal muscles【骨骼肌】
- as a _______________ building block【組件】 of larger molecules
- cellulose【纖維素】 as a source of _______________ dietary fibre【膳食纖維】
- can’t be digested【被消化】 in human body
- keeps the _______________ digestive system【消化系統】 healthy
|
| 6. | Lipids【血脂】
Organic food substances【有機物質】
- made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
- _______________ insoluble【不溶於】 in water
- _______________ soluble【溶於】 in organic solvent【有機溶劑】. For example, _______________ ethanol【乙醇/酒精】
Triglycerides【甘油三酸酯】
One main group of lipids is triglycerides.
Saturated fats【飽和脂肪】
- at room temperature -> _______________ solid
- main sources -> animals
- examples -> butter, lard【豬油】, cheese and fatty meat
Unsaturated fats【不飽和脂肪】
- at room temperature -> _______________ oily
- main sources -> plants and fish
- examples -> corn oil, olive oil, and salmon
|
Saturated fats【飽和脂肪】 |
Unsaturated fats【不飽和脂肪】 |
| At Room Temperature |
_______________ solid |
_______________ oily |
| Main Sources |
animals |
plants and fish |
| Examples |
butter, lard【豬油】, cheese and fatty meat |
corn oil, olive oil and salmon |
Metabolism【代謝】 of lipids
A triglyceride molecule is formed from one _______________ glycerol【甘油】 molecule and three _______________ fatty acid【脂肪酸】 molecules by condensation【凝結】. Before absorbed【吸收】 directly in the digestive tract【消化道】, it must first be broken down【分解】 into smaller molecules by _______________ hydrolysis【水解】, in the presence of _______________ water and a suitable _______________ enzyme【酶】.
Function of lipids
- source of energy
- 1 gram of lipid produces _______________ 38.9 kJ of energy
- excess lipids
- stored in _______________ adipose tissues【脂肪組織】 in the body as an energy reserve
- under the skin as _______________ subcutaneous fat【皮下脂肪】 which acts as an insulating layer【絕緣層】 to reduce heat loss
- around _______________ internal organs【內臟】 to act as shock-absorbers【減震器】.
- transport and storage of _______________ fat-soluble vitamins【脂溶性維他命】
- _______________ cholesterol【膽固醇】 is a raw material for producing lipid hormones【脂質荷爾蒙】
Bad fats and good fats
|
Bad fats |
Good fats |
|
Saturated fats |
Unsaturated fats |
| Effects |
- increase the level of bad cholesterol【膽固醇】 in the _______________ blood
- bad cholesterol deposits【沉積】 on the inside walls of _______________ blood vessels【血管】 and block【堵塞 】 the _______________ blood flow【血液流動】
- eventually, lead to _______________ cardiovascular diseases【心血管疾病】
|
- lower the _______________ blood glycerol level【血糖水平】
- control _______________ blood clotting【血液凝結】
- lower _______________ blood pressure【血壓】
|
| Examples |
animal fats, cheese, milk …… |
egg, avocado, almond …… |
Bad Fats / Saturated Fats
- effects
- increase the level of bad cholesterol【膽固醇】 in the _______________ blood
- bad cholesterol deposits【沉積】 on the inside walls of _______________ blood vessels【血管】 and block【堵塞 】 the _______________ blood flow【血液流動】
- eventually, lead to _______________ cardiovascular diseases【心血管疾病】
- examples
- animal fats, cheese, milk ……
Good Fats / Unsaturated Fats
- effects
- lower the _______________ blood glycerol level【血糖水平】
- control _______________ blood clotting【血液凝結】
- lower _______________ blood pressure【血壓】
- examples
|
| 7. | Proteins【蛋白質】
Organic substances【有機物質】
- large _______________ complex【複雜】 molecules
- made up of _______________ carbon, _______________ hydrogen, _______________ oxygen and _______________ nitrogen【氮】.
- some contain _______________ sulphur【硫】
- amino acid【氨基酸】
- _______________ subunits【亞單位】 of protein
- human requires _______________ 20 different types of amino acid to _______________ synthesize【合成】 proteins.
- 11 types are _______________ non-essential【非必須】 amino acids, which can be made using other compounds【化合物】 in our body.
- 9 types are _______________ essential【必需】 amino acids, which cannot be made in our body and must be included in our _______________ diet.
|